Ever had one of those moments where you’re staring at a blinking console in the middle of a noisy manufacturing floor, and you just know something’s amiss with the system? The hum of automated manufacturing equipment and the subtle vibrations from the servo mechanisms all blend into a chaotic symphony, but that one glitch—it’s like a tiny crack in a finely tuned orchestra.
If you’ve been working with Loguytren components or involved in industrial automation systems, you probably already have a sense of the unseen challenges hiding beneath the polished surface.
These glitches—what we’ll call Loguytren problems—aren’t just annoying bugs; they’re puzzle pieces in the vast picture of manufacturing precision and reliability.
This article is for anyone tangled in the wires of mechanical-electronic interface systems, battling the ghost of calibration drift or fending off electromagnetic interference that creeps like static in the background of production lines.
Let’s dive deep, get a bit wonky, and figure out what’s really causing these headaches, how you can spot them early, and what keeps the cogs turning smoothly.
What Exactly Are Loguytren Problems?
The phrase Loguytren problems might sound like some obscure medical condition, but in the world of manufacturing, it refers to a set of complex, often interrelated malfunctions affecting Loguytren technology embedded within precision machinery.
These problems typically manifest in system faults such as firmware integration failures, command execution delays, and data reporting inconsistencies that degrade product quality and bloat maintenance costs.
Think of it like this: your manufacturing line relies on countless tiny sensors, sensor arrays, and microprocessors all harmonized through multi-axis synchronization controls.
When even one mechanical interface starts wearing down or a single sensor suffers from calibration issues due to thermal expansion and contraction, it creates a ripple effect. Suddenly, the quality assurance process flags more rejects, downtime increases, and your shiny production efficiency metrics start nosediving.
If you’re scratching your head wondering how such microscopic changes—say, microscopic vibration displacement or subtle firmware regression testing errors—can topple entire systems, you’re not alone. The devil’s always in the details here.
Causes of Loguytren Problems: The Hidden Saboteurs
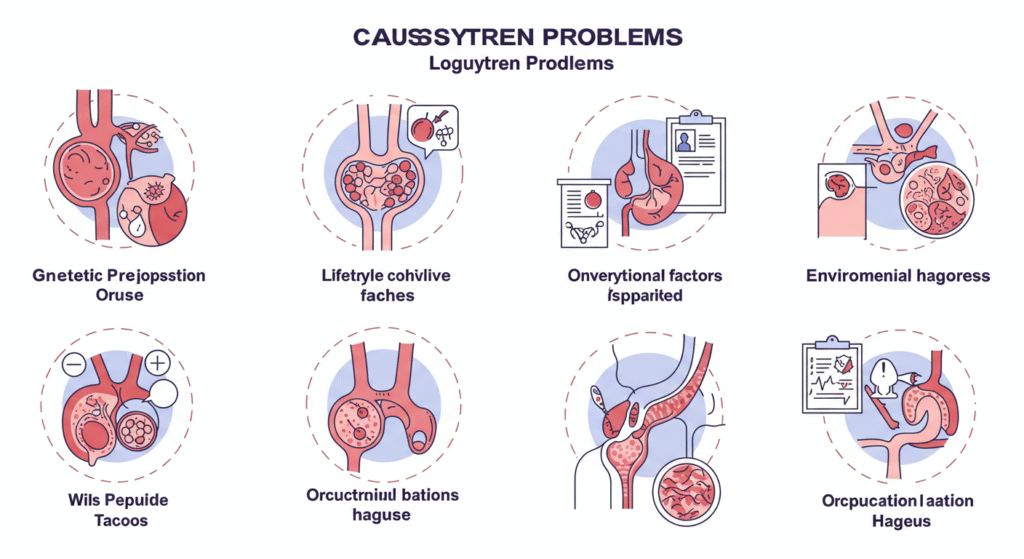
Understanding the root causes is like peeling an onion—layers upon layers. Let’s peel back some of the most common triggers:
1. Environmental Factors in Manufacturing
It’s easy to underestimate how much the environment influences manufacturing automation lines. Slight temperature and humidity fluctuations can mess with measurement precision and cause sensor degradation. Imagine a clean room protocol that isn’t strictly followed—dust particles and particulate contamination accumulate, impacting sensor array optimization and skewing data.
Not just that, electromagnetic interference impact—from nearby heavy machinery or wireless signals—can induce communication protocol conflicts, leading to false positives or reading errors that confuse the system.
2. Firmware Integration and Compatibility
Ah, the saga of firmware. Updating or integrating firmware across devices sounds routine, but a slight firmware compatibility mismatch or firmware regression testing oversight can cause the whole system to stumble. Firmware integration failures often result in system crashes or command execution delays, slowing down your production accuracy and elevating product rejection rates.
3. Mechanical Wear and Calibration Drift
Over time, physical components—especially in high-precision contexts like microchip fabrication or automotive assembly—experience mechanical interfaces wear. The tiniest deviation caused by thermal cycling effects or constant vibration spectrum analysis revealing hidden faults can cause significant calibration drift, throwing off your precision recalibration protocols.
Read This Blog: https://cozygreets.com/the-rise-of-zryly-com-internet/
4. Sensor and Signal Degradation
Sensors, the eyes and ears of your system, don’t last forever. Sensor deterioration leads to inaccuracies, while reading errors due to sensor replacement vs. optimization decisions become a daily conundrum. The choice between swapping out a sensor or optimizing signal processing through adaptive filtering and signal processing algorithms often impacts maintenance cost reduction and operational lifespan extension.
5. Contamination and Cleanliness
From the Manufacturing Technology Quarterly (2023 survey), contamination remains a silent killer in manufacturing environments. Even the most minute particulate matter can wreak havoc on sensor readings and mechanical operations. Strict clean room protocols, environmental control measures, and particulate contamination monitoring are indispensable.
Solutions: How to Combat Loguytren Problems Like a Pro
Addressing these issues demands a cocktail of technical savvy, vigilant maintenance, and strategic upgrades.
Proactive Preventive Maintenance
The age-old wisdom of “nip it in the bud” holds true. Scheduled inspection schedules, combined with predictive maintenance AI, help catch issues before they snowball. Tools like the LoguTech Diagnostic Suite offer AI-assisted analysis and remote diagnostic capabilities, meaning you don’t have to wait for a full-blown breakdown to act.
Calibration and Environmental Control
Precision recalibration isn’t a one-time thing; it’s a continuous battle. Implementing laser-guided alignment, temperature-controlled calibration, and vibration-isolated adjustment ensure your system stays razor-sharp. Meanwhile, maintaining stringent environmental assessment protocols—monitoring temperature and humidity fluctuations, performing electromagnetic field mapping, and adhering to clean room protocols—mitigates external impact.
Firmware Management and Testing
Keeping firmware updated yet stable involves meticulous firmware regression testing and configuration management. Instituting firmware rollback options can save the day if a new update introduces unexpected system faults. Working closely with vendors or relying on machine learning algorithms to analyze operational data analysis and error logs aids in identifying patterns before they escalate.
Redundancy and Optimization
Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Incorporating redundancy implementation in critical components and optimizing sensor arrays with adaptive filtering reduces false alarms and improves reliability. It’s a balancing act between cost and robustness but essential for high-stakes manufacturing where product quality can’t be compromised.
Staff Training and Certification
Even the best equipment needs well-trained hands. Investing in staff training and certification around diagnostic tools, maintenance history tracking, and knowledge refreshers ensures your team can act swiftly and accurately. Skilled operators can spot subtle signs of mechanical-electronic interface systems malfunction before they snowball into full outages.
Case Study: Semiconductor Manufacturer in Taiwan
One of the leaders in microchip fabrication, a prominent Taiwanese semiconductor manufacturer, faced recurring sensor degradation and calibration drift problems that affected yield rates. By integrating statistical process control, deploying AI-assisted analysis, and refining precision recalibration protocols—including laser-guided alignment and vibration dampening—they successfully reduced downtime by 30% and cut maintenance costs by nearly 20%. Their adoption of remote diagnostic capabilities enabled engineers to troubleshoot from afar, saving crucial time during critical production cycles.
This case exemplifies how combining technology, environment control, and human expertise creates a blueprint for tackling Loguytren problems in any advanced manufacturing setting.
Prevention: Staying Ahead of the Curve
It’s always better to prevent than to repair. The following strategies form the backbone of a preventative culture in manufacturing:
- Implement continuous environmental control measures to minimize thermal cycling effects and electromagnetic interference.
- Regularly update and test firmware, but ensure firmware rollback options and configuration management are in place.
- Schedule frequent inspection schedules and use predictive maintenance AI to identify faults early.
- Optimize sensor array design and perform routine sensor replacement vs. optimization assessments.
- Maintain a clean, controlled environment following clean room protocols and minimize particulate contamination.
- Train staff rigorously, keep certifications current, and promote cross-functional communication for rapid problem resolution.
- Leverage data from operational data analysis, error logs, and fault histories to spot trends and plan improvements.
Bringing It All Together
Understanding and tackling Loguytren problems requires looking beyond just the immediate fault. These issues interlace environmental dynamics, firmware intricacies, mechanical wear, and human factors into a complex web. But with smart strategies—like those embraced by top-tier manufacturers in automated manufacturing lines—the benefits include improved production efficiency, reduced maintenance costs, and enhanced product quality.
Navigating these challenges doesn’t have to be a solitary quest. Whether you’re an engineer staring down a system crash or a plant manager reviewing a Manufacturing Technology Quarterly (2023 survey), remember that this is a dynamic field where machine learning algorithms, AI, and advanced diagnostic suites like LoguTech are evolving to make life easier.
How do you approach Loguytren technology problems in your workspace? Have you tried any of these solutions or faced unique challenges? Share your stories or tips below—I’d love to hear how you’re keeping your production lines humming smoothly!
